Solar at Tufts
Tufts’ earliest clean energy installation dates back to 1999 with 500 Watts of photovoltaics on Fairmont House, a small campus residence hall. Since then, Tufts has installed solar panels on residential and academic buildings across its Medford/Somerville campus. Through PowerOption’s Large Scale Solar program, two large ground-mounted photovoltaic systems were installed on the Grafton campus in 2017. In 2024, Tufts announced its participation in a first-of-its-kind aggregated renewable energy purchase that reduced energy-related emissions on the Boston health sciences campus by 40%.
Tufts funds solar installations in several ways: capital expenditure, grants, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPA)/Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPA). PPA's and VPPA's are mechanisms that allow Tufts to support solar energy development on a larger scale while maximizing the impact of our funding and carbon emissions reduction. Watch our solar energy webinar to hear more about how we use these solar energy strategies at Tufts.
Keep reading to learn where each solar array at Tufts is located, when it was installed, how it was funded, and how much energy it produces.
Big Elm Virtual Power Purchase Agreement
Using a procurement model known as a virtual power purchase agreement (VPPA), Tufts supported the creation of 20,000 megawatt hours of new solar energy in Texas – enough to power 1,800 homes a year. As a result of this project, Tufts reduced energy-related emissions on the Boston health sciences campus by 40%.
Year Installed: 2024
Funding: Virtual Power Purchase Agreement with Apex Clean Energy in collaboration with the Consortium for Climate Solutions, a first-of-its-kind group of higher education institutions, healthcare systems, nonprofit organizations, and a municipality in Cambridge and Boston, leveraging collective purchasing power to invest in renewable energy.
Power Produced: 7.6 MW (20,000 MWh annually)
Community Solar
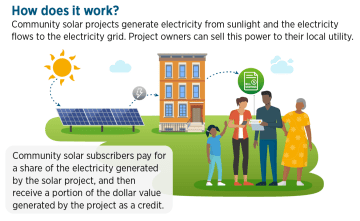
Credit: U.S. Department of Energy
Tufts supports multiple community solar projects across Massachusetts to support the equitable distribution of renewable energy. Community solar refers to solar arrays that are owned by multiple people or organizations. Particularly for people who cannot afford to pay for solar alone, community solar reduces cost barriers and increases the accessibility of renewable energy.
Tufts partnered with Power Options in 2020 to help create community solar arrays across Massachusetts to support the equitable distribution of renewable energy. In return, Tufts receives cost savings on its energy bills.

Cummings School
Campus: Grafton
Year Installed: Construction for this project began in 2015. The panels were activated in 2017.
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with Sun Edison (has since switched to NRG Energy)
Power Produced: 3,800 kW

Dowling Garage
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2014
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with SunBug Solar
Power Produced: 99 kW (125,000 kWh annually) Live data on energy generation from the Dowling
Garage can be seen here.
Gantcher Center
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2019
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with Solect Energy
Power Produced: 340 kW (390,000 kWh annually)

Hodgdon Hall
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2018
Funding: Grant funded by Tufts Green Fund ($6,500), Tufts University ($5,500), and SunBug Solar ($10,000)
Power Produced: 2700 kWh annually with 6 kWh of battery storage (enough to power 1,000 phones!). This is a Tufts Energy Group project that charges student electronic devices on the patio and common room.

Joyce Cummings Center
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2023
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with Solect Energy
Power Produced: 89.8 kW (102,600 kWh annually)

Lewis Hall
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2018
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with Solect Energy
Power Produced: 83.2 kW (100,000 kWh annually)

Tsungming Tu Complex
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2018
Funding: Power Purchase Agreement with Solect Energy
Power Produced: 52.36 kW (61,000 kWh annually)
Sophia Gordon Hall
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2006
Funding: Grant funded by the Massachusetts Technology Collaborative ($500,000) with additional funds provided by Tufts.
Power Produced: 23.8 kW (25,000 kWh annually)
SoGo solar reduces approximately 17.7 Metric tons carbon dioxide equivalent emissions per year,
which is equal to 2 homes' energy use each year.
Calculated with the Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies
Calculator.
12 Bellevue St.
Campus: Medford/Somerville
Year Installed: 2019
Funding: $40,200 provided by donor
Power Produced: 12 kW DC (13,000 kWh annually)

